4. Control strategy of microgrid
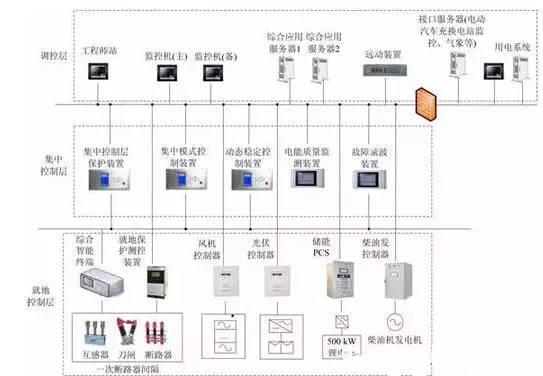
The overall control strategy of microgrid
There are two main control strategies commonly used in micro-grids, master-slave operation and peer-to-peer control.
Master-slave control mode: A distributed power supply (or energy storage device) in the microgrid adopts V/f control to provide voltage and frequency reference for the microgrid, while other distributed power supplies adopt PQ control.
Peer-to-peer control mode: multiple controllable distributed power sources (or energy storage devices) involved in voltage and frequency regulation and control in the microgrid have the same status in control. Usually, Pf and QV droop control methods are selected, according to the distribution -Type power access point for local information control.
Control strategy of micro power supply
Since the microgrid is based on power electronic technology, the micro power supply in it has high controllability. The control strategy for the micro power supply can be divided into three types: constant power control, droop control and constant voltage and constant frequency control.
Constant power control (PQ control): Realize active and reactive power control = reference value. When distributed power generation systems such as photovoltaics and wind turbines adopt maximum power tracking control, it belongs to constant power control. When the microgrid is connected to the grid, the grid provides voltage and frequency reference, and each distributed power supply generally adopts constant power control. Of course, some controllable distributed power sources can also use f-P and V-Q droop control methods, which can support the grid voltage and frequency when the grid voltage amplitude and frequency decrease.
Constant voltage/constant frequency control: control voltage and frequency.
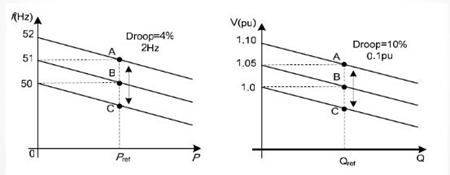
Droop control: The frequency droop characteristic curve (DroopCharacter) similar to that of the traditional generator is selected as the control method, namely, the stable frequency and voltage are obtained through P/f droop control and Q/V droop control. This control method is The active power and reactive power output by the micro-sources in the micro-grid are controlled separately, without the need for communication coordination between units, and the goal of micro-source plug-and-play and peer-to-peer control is achieved.
5. Two operating modes of microgrid
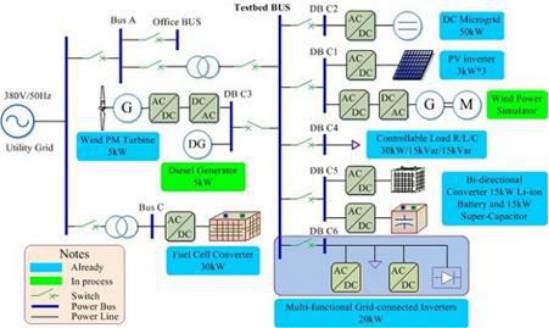
There are two typical operation modes of microgrid: under normal circumstances, the microgrid and the conventional distribution network are connected to the grid, which is called the networking mode; when a grid failure or power quality is not met, the microgrid will be disconnected from the grid in time The independent operation is called island mode. The switching between the two must be smooth and fast. Compared with the external large power grid, the micro-grid is a single controlled unit, and can meet the requirements of users for power quality and power supply safety at the same time. The power supply inside the microgrid is mainly responsible for energy conversion by power electronic devices and provides necessary control. (1) Grid-connected operation: the micro-grid is connected to the large public grid, the micro-grid breaker is closed, and the electric energy is exchanged with the main grid power distribution system. The photovoltaic system is connected to the grid to generate electricity. The energy storage system can perform charging and discharging operations in grid-connected mode. During grid-connected operation, the control device can be switched to off-grid operation mode.
(2) Off-grid operation: also known as island operation, refers to the operation mode that is disconnected from the main grid power distribution system when the grid fails or is required by the plan, and consists of DG, energy storage devices and loads. The energy storage converter PCS works in the off-grid operation mode to continue to supply power to the microgrid load. The photovoltaic system continues to generate power due to the restoration of power supply from the busbar. The energy storage system usually only supplies power to the load.
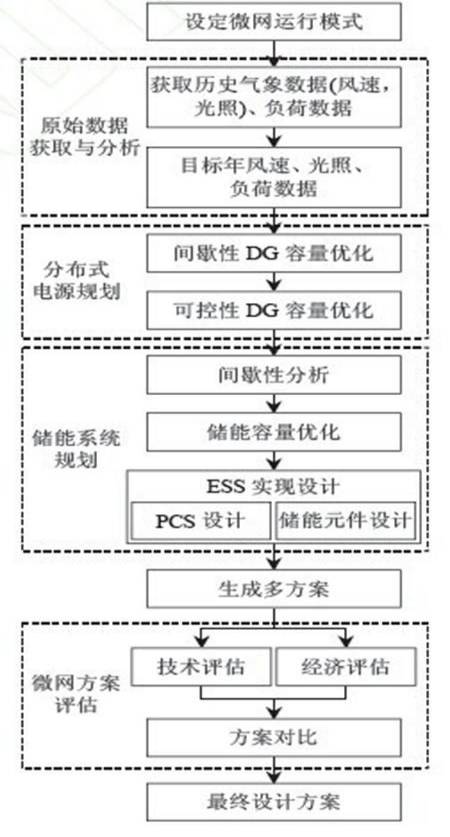
6. Microgrid planning